Does every step hurt when your heel-to-toe movement involves the big toe? Then you may have hallux rigidus. This term refers to a restriction of movement in the big toe caused by osteoarthritis which results in severe pain. This condition is usually detected at a later stage in men, but very early in women. That is because the painful symptoms manifest earlier in women based on tighter and higher footwear. This, in turn, allows earlier treatment to positively influence the progression. The earlier treatment is started, the better the prognosis.
What are the causes of hallux rigidus?
Hallux rigidus (Latin: hallux meaning big toe, rigidus meaning stiff or heavy) is one of the most common conditions of the big toe. It is based on osteoarthritis of the metatarsophalangeal joint. Even though the actual triggers for hallux rigidus have not been fully explained yet, various risk factors are known. These include:
- ill-fitting shoes (too small and narrow)
- foot misalignments
- obesity
- injuries
- congenital factors
- growth anomalies
The metatarsophalangeal joint is subjected to alot of strain even in healthy people because the heel-to-toe movement during walking takes place via the big toe. Disproportionate strain based on one or several of the risk factors mentioned will cause damage in the long term. The joint is damaged which will eventually result in painful osteoarthritis and inflammatory processes. As a consequence, the joint space becomes increasingly narrow until it fully closes up and the bones rub on each other.
Symptoms of hallux rigidus: what signs should I look out for?
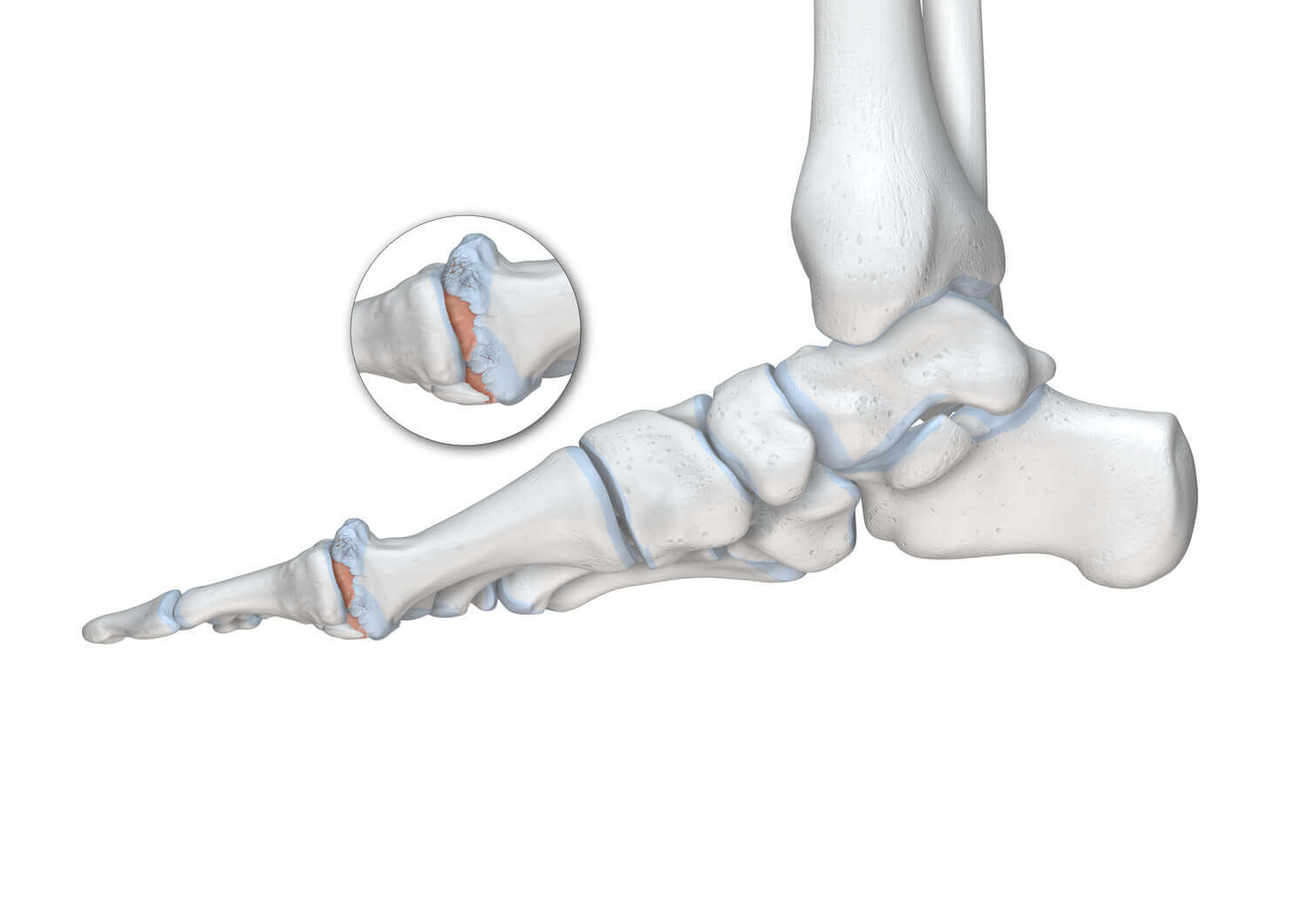
Years may go by until the big toe has become completely rigid. During this time, various symptoms may occur. The first typical signs of osteoarthritis of the foot include:
- pain, usually temporary
- swelling of the big toe
- twitching muscles in the affected foot
- development of calluses
- rubbing sounds during movement
These symptoms can differ in severity but always lead to a limitation in quality of life. Without treatment, the condition will not stop. Healing already existing damage to the bone is not possible either. But targeted treatment can alleviate the symptoms and slow down the progression of the condition.
Diagnosing and treating hallux rigidus
To diagnose hallux rigidus with certainty, the physician will examine the affected toe and ask the patient questions relating to symptoms and the previous development of the problems. The physician will also try to find out whether hallux rigidus has already occurred in the patient’s family (family history).
The course of the hallux rigidus treatment will depend on the stage of the condition. Initially, the patient’s pain will be alleviated with medication. Pain medication to be taken orally as well as anti-inflammatory creams that can be applied locally are usually available for this.
Physiotherapy including manual therapy and foot exercises can also alleviate symptoms and counteract deterioration.
Other options include balneotherapy (e.g. sulfur or radon baths) which are designed to counteract signs of wear and inflammatory joint problems. Compresses and hot foot baths are also common methods contributing to the alleviation of pain.
In severe cases, infusion therapy is also used. This involves local anesthetics and medication containing cortisone being directly injected into the affected region. The advantage is that the patient usually notices an immediate improvement. Because of the increased risk of infection, however, this treatment is rarely the first choice.
Surgery is possible but should be the last resort for treating hallux rigidus.
Treating hallux rigidus early
When you notice the first signs of osteoarthritis in the metatarsophalangeal joints, it is highly recommended you obtain ways of relief, such as foot orthoses, immediately to tackle these problems. In this way, the progression of the condition can be positively influenced as early as possible. Otherwise, those affected can expect that the joint will become completely stiff one day.
To provide relief and pain alleviation, the ErgoPad foot orthosis has proven effective. It reduces strain on the affected joint, thus preventing further irritation. This may help delay surgery.
Hallux rigidus: optimizing treatment with foot orthoses
Even tried-and-tested as well as targeted treatments of hallux rigidus will not result in significant improvement if the affected area is not protected. That is why the affected foot is usually immobilized for the duration of the treatment to relieve the joint. This helps stop inflammatory processes, and stiffening can be prevented.
To provide relief, a reinforcement element is integrated into the ErgoPad redux hallux foot orthosis that reduces the deviation of the joint. The foot orthosis can minimize pain in this way. The reinforcement element counteracts inappropriate mechanical stress of the foot, thus preventing painful movements. At the same time, it features viscoelastic properties that prevent the heel from lifting out of the shoe, therefore maintaining a largely natural heel-to-toe movement.
Depending on requirements, the foot orthoses are available for the right or left foot, or as a pair. Accordingly, they feature the reinforcement element described above. In cases of one-sided hallux rigidus, the foot orthosis without reinforcement element has the identical material height and cushioning and is also equipped with an arch support. Not only does this ensure the same sensation when walking, it also counteracts excessive strain on the other side at the same time. The best results are achieved with a combination of foot orthoses and physical treatment as well as medication.


